library(rstac)
library(gdalcubes)
library(stars)
library(tmap)
library(dplyr)
earthdatalogin::gdal_cloud_config()
gdalcubes::gdalcubes_options(parallel = TRUE)1: Satellite data
box <- c(xmin=-123, ymin=37, xmax=-121, ymax=39)
start_date <- "2022-06-01"
end_date <- "2022-08-01"
items <-
stac("https://earth-search.aws.element84.com/v0/") |>
stac_search(collections = "sentinel-s2-l2a-cogs",
bbox = box,
datetime = paste(start_date, end_date, sep="/"),
limit = 100) |>
ext_query("eo:cloud_cover" < 20) |>
post_request()col <- stac_image_collection(items$features, asset_names = c("B08", "B04", "SCL"))
cube <- cube_view(srs ="EPSG:4326",
extent = list(t0 = start_date, t1 = end_date,
left = box[1], right = box[3],
top = box[4], bottom = box[2]),
dx = 0.001, dy = 0.001, dt = "P1M",
aggregation = "median", resampling = "average")The SCL data layer in Sentinel is one of three ‘quality assurance’ layers provided in this data catalog. Table 3 in this description of the Sentinel-2 Level2A Specifications summarizes the classification codes (Cloud shadows, medium probability cloud, high probability cloud). An image mask basically drops these bad pixels.
mask <- image_mask("SCL", values=c(3, 8, 9)) # mask clouds and cloud shadows
data <- raster_cube(col, cube, mask = mask)ndvi <- data |>
select_bands(c("B04", "B08")) |>
apply_pixel("(B08-B04)/(B08+B04)", "NDVI") |>
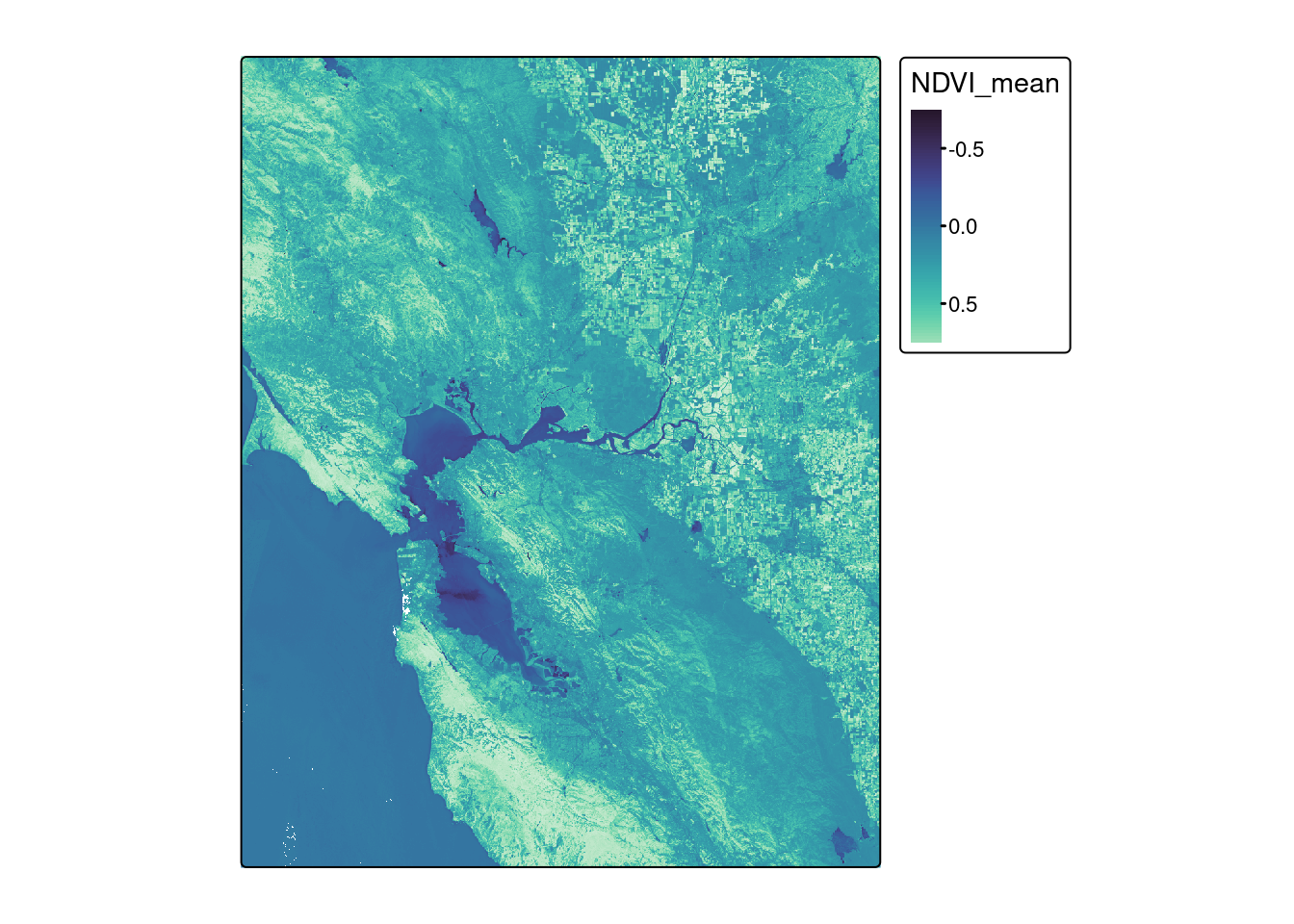
reduce_time(c("mean(NDVI)")) ndvi_stars <- st_as_stars(ndvi)mako <- tm_scale_continuous(values = viridisLite::mako(30))
fill <- tm_scale_continuous(values = "Greens")
tm_shape(ndvi_stars) + tm_raster(col.scale = mako)stars object downsampled to 1000 by 1000 cells.